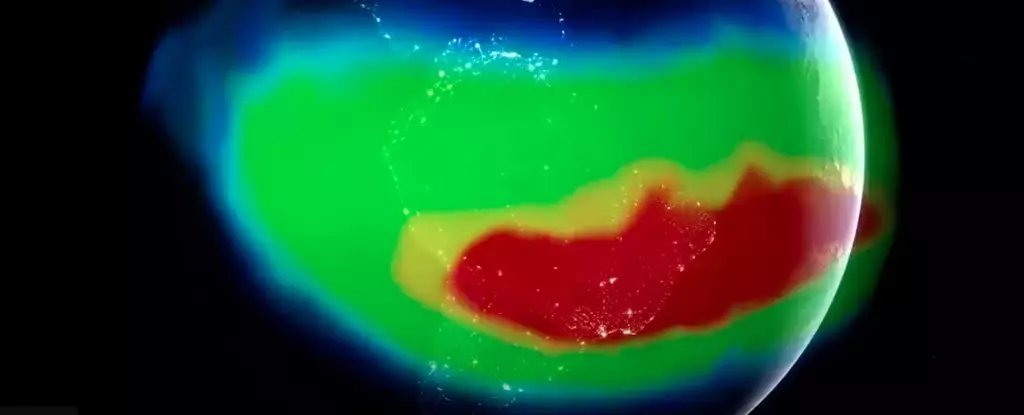
In recent years, scientists have increasingly turned their attention to a peculiar feature in the Earth’s magnetic field: the South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA). This phenomenon, dubbed a “dent” in the magnetic shield of our planet, extends between South America and southwest Africa. For researchers, particularly those at NASA, the SAA represents not only a source of concern but also an intriguing opportunity for deeper scientific examination. This article delves into the origins, implications, and ongoing research surrounding this anomaly.
The Earth’s magnetic field is primarily generated by the dynamic movement of molten iron within its outer core. As these fluids swirl, they produce electrical currents, which in turn create the magnetic field that protects our planet from harmful solar radiation. However, this field does not exist uniformly; localized disturbances can occur, resulting in regions of varying magnetic intensity.
To comprehend the SAA, it is essential to examine the geological features contributing to its existence. A significant factor is a geological formation known as the African Large Low Shear Velocity Province, located about 2,900 kilometers below the surface of Africa. This dense rock layer disrupts the flow of materials in the core, consequently affecting the generation of the magnetic field. As noted by NASA geophysicist Weijia Kuang, the SAA showcases a specific inversion in the magnetic polarity that strengthens in this region, leading to the observed reduction in field intensity.
Impact on Spacecraft and Technology
One of the most alarming effects of the South Atlantic Anomaly is its potential impact on spacecraft operations. As satellites orbit the Earth, many pass through this magnetic disturbance, exposing their systems to heightened risks from charged solar particles. When these high-energy protons collide with spacecraft, they can cause electronic malfunctions, leading to data loss or even irreversible damage.
NASA has developed protocols that require satellite operators to temporarily shut down sensitive systems before traversing the anomaly to counter these risks. While many encounters will only yield minor glitches, the possibility of major failures makes the SAA a focal point for ongoing monitoring and caution.
Scientific understanding of the South Atlantic Anomaly is continually evolving, with new studies shedding light on its behavior and implications. An important finding came from research conducted by heliophysicist Ashley Greeley in 2016, which revealed that the anomaly is not a static feature but one that drifts over time. This movement was subsequently confirmed by further observations from CubeSats as recently as 2021.
Even more striking is evidence suggesting that the anomaly is undergoing a process of division. Recent studies indicate that the SAA may be splitting into two distinct centers of reduced magnetic intensity, which raises questions about its future evolution. Researchers continue to explore the consequences of such changes, which could have far-reaching implications both in terms of magnetic field dynamics and our technological infrastructure in low-Earth orbit.
The Historical Context and Future Outlook
What’s particularly fascinating about the SAA is that it is not a mere recent occurrence but rather part of a more extensive historical trend. A study published in July 2020 suggests that anomalous regions like the SAA have been present for millions of years, indicating patterns that may repeat themselves over vast geological time scales. The possibility that the SAA is a recurrent phenomenon invites a broader inquiry into magnetic field behaviors, including possible correlations with past magnetic pole reversals.
Despite a wealth of information, there remain numerous unanswered questions. The implications of the anomaly’s behavior on Earth’s magnetic field stability and the potential ramifications for global navigation and communication systems warrant close scrutiny. As NASA researchers, along with global counterparts, continue their research endeavors, we can expect ongoing developments that will deepen our understanding of this unique magnetic phenomenon.
As the South Atlantic Anomaly continues to capture the interest of scientists, its implications stretch far beyond the intriguing field anomalies themselves. This magnetic oddity offers a lens through which to examine Earth’s geological processes and the vulnerabilities of our technological systems within space. The consistent monitoring by organizations like NASA ensures that we remain informed about the evolving dynamics of the SAA while furthering our understanding of one of nature’s more enigmatic phenomena. As we stand on the brink of more discoveries, the importance of ongoing research and awareness cannot be overstated.

Leave a Reply