The phenomenon of Arctic Amplification, driven by human activities, has caused Greenland to warm at a faster rate than the rest of the world. This accelerated warming has resulted in increased ice sheet melting, posing a significant threat to global coastal areas and ecosystems. The drivers behind Arctic Amplification, such as local climate feedback processes, heat release from the Arctic Ocean, and energy transport from the south, play a crucial role in understanding the future impacts of climate change.
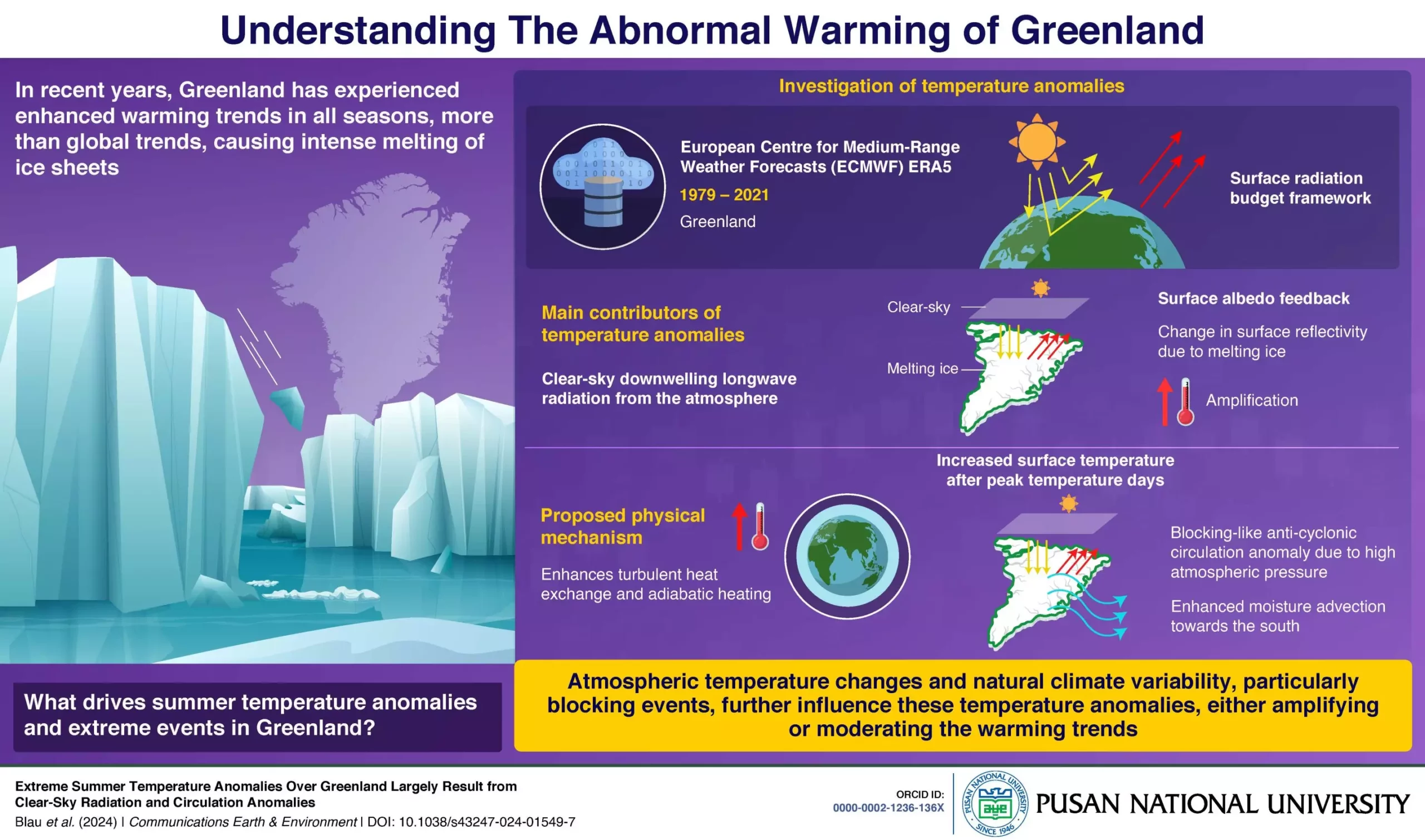
A recent study led by Professor Kyung-Ja Ha and her team from Korea sought to investigate the anomalous warming trends in Greenland from 1979 to 2021. By focusing on year-to-year perturbations of the surface energy budget, the researchers aimed to explain the extreme temperatures experienced in Greenland. Their findings, published in the journal Communications Earth & Environment, shed light on the dominant factors contributing to Greenland’s surface warming.
The researchers identified clear-sky downwelling longwave radiation and surface albedo feedback as the primary factors driving Greenland’s warming trends. Increases in clear-sky radiation, which is the heat radiated by the atmosphere to the surface on clear-sky days, were found to be linked to rising atmospheric temperatures. In warm years, the combination of increased surface temperatures, tropospheric warming, and moisture transport from the south led to a high-pressure system that trapped warm conditions, intensifying ice melting and creating a feedback loop.
The study also highlighted the role of natural climate variability, particularly the Greenland blocking index, in either amplifying or moderating warming trends. Different modes of natural climate variability can lead to extreme temperature events, further accelerating ice sheet melting and contributing to rapid sea-level rise. Understanding the interplay between human-driven climate change and natural climate variability is essential for predicting the future development of the Greenland ice sheet.
By uncovering the drivers of Greenland’s extreme summer temperatures, this study provides crucial insights that can inform strategies to mitigate further degradation of the Greenland ice sheet. The findings emphasize the urgent need to address climate change and its impacts on the Arctic region, as continued warming could have significant consequences for global sea levels and coastal ecosystems. Overall, a comprehensive understanding of Arctic Amplification and its effects on Greenland is vital for developing effective solutions to combat climate change.
The research on Greenland’s extreme warming trends highlights the complex interactions between human-driven climate change, natural climate variability, and the Arctic environment. By delving into the specific factors driving Greenland’s warming, scientists can better predict future climate impacts and develop strategies to address the challenges posed by Arctic Amplification. The urgency of the situation calls for immediate action to mitigate the effects of climate change and protect the fragile ecosystems of the Arctic region.

Leave a Reply