Small electric motors play an indispensable role in our everyday lives. From household appliances like washing machines and refrigerators to essential components in modern vehicles, these motors are at the heart of a multitude of systems. Although each motor operates at a low energy consumption level individually, their collective impact can be substantial. Efficient operation of these motors becomes not merely an advantage but a necessity, especially in our mission toward sustainable energy consumption. With continued advancements in technology, the potential for significant energy savings has never been more tangible, inspiring research efforts aimed at optimizing motor performance.
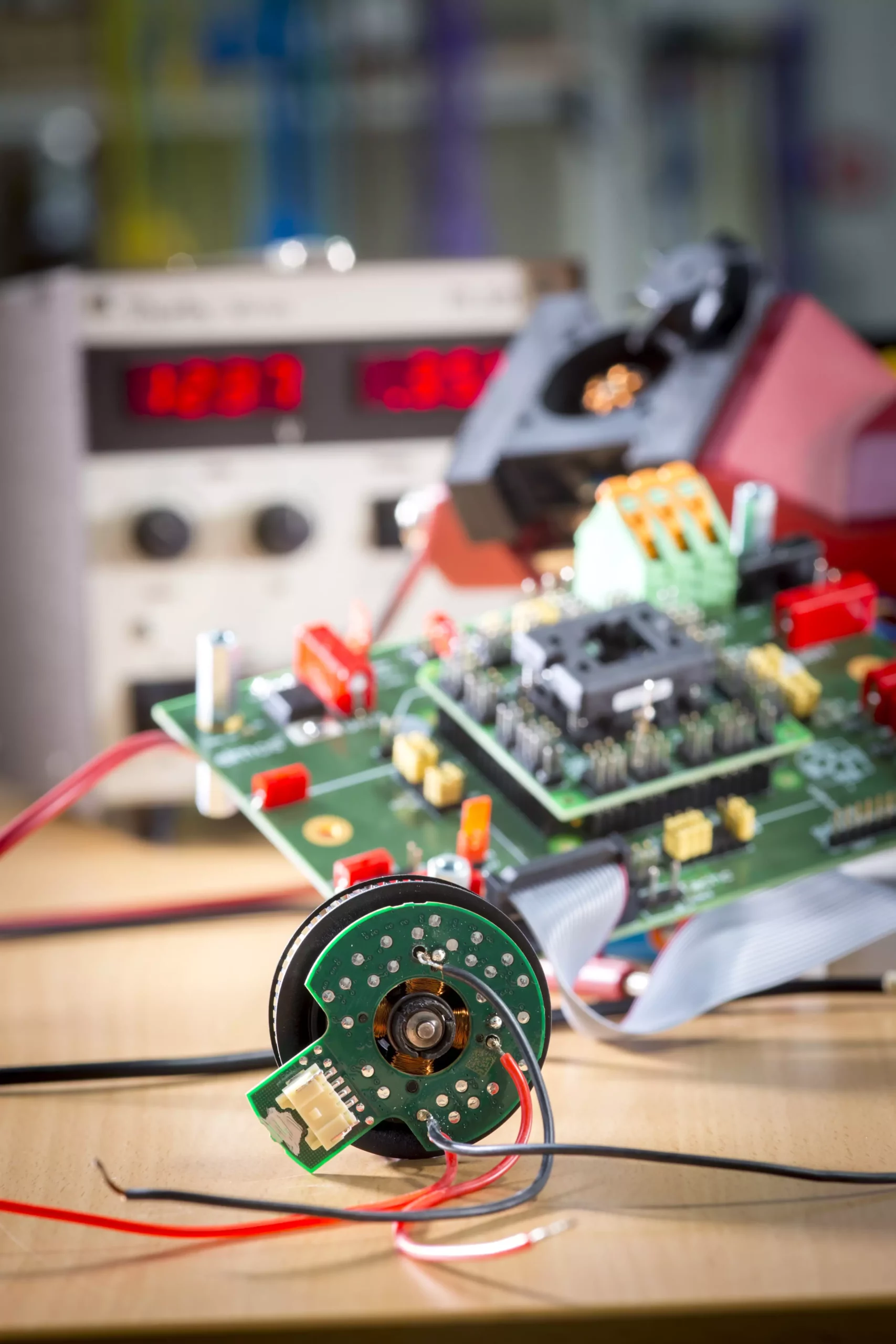
Recently, a groundbreaking initiative known as the “CD Laboratory for Brushless Drives for Pump and Fan Applications” was helmed by Annette Mütze from the Electric Drives and Power Electronic Systems Institute at Graz University of Technology (TU Graz). The team’s research has focused on exploring the latent potential within small electric motors, specifically targeting the aspects related to design, control technology, and manufacturing practices. Their work has culminated in the development of brushless integrated drives that not only consume less energy but also operate with greater quietness and reduced weight—factors that are increasingly significant in vehicle design and household appliance functionality.
One of the remarkable insights from Mütze’s research revolves around the reduction of cogging torque—a phenomenon that can lead to unwanted vibrations and noise in electric motors. By employing innovative techniques such as skewing and slotting the claws of claw pole motors, the team achieved a notable decrease in these unwanted effects. Mütze elaborates, stating that this adjustment has led to a striking 70% reduction in noise, transforming the user experience. The increasingly quiet operation of appliances and vehicles represents a substantial improvement not just for consumers seeking comfort, but also for applications where noise minimization is critical.
The enhancement of overall efficiency in electric motors can be attributed to the novel regulation of current flow. Traditional pulse width modulation (PWM) techniques, although effective, often lead to energy losses due to frequent switching operations required to maintain a desired current output. However, Mütze’s team has successfully streamlined this process by simplifying the switching mechanism—activating the motors only once per desired pulse. This methodological shift significantly minimizes the energy wastage resulting from switching losses, and particularly improves performance at lower currents, presenting a competitive edge over conventional PWM-controlled motors.
In addition to energy efficiency and noise reduction, Mütze’s team has brought forth innovations concerning the physical structure of these motors through the use of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) technology. By integrating the windings that generate the magnetic fields into printed circuit boards, the production process has been greatly automated. This advancement not only simplifies manufacturing logistics but also reduces costs. The introduction of 3D-printed ferrite cores into these PCB motors has optimized the magnetic flux flow, enabling the use of more economical ferrite magnets compared to traditional counterparts.
The innovations spearheaded by Annette Mütze and her team at TU Graz signify a pivotal moment in the evolution of small electric motors. As technology continues to advance, the implications of these advancements extend far beyond academic interest; they hold the potential to transform energy consumption practices on a global scale. By enhancing efficiency while simultaneously cutting costs, such innovations lay the foundation for sustainable practices in both household and automotive sectors, thereby supporting broader efforts toward environmental conservation. As industries adopt these optimized systems, the results could lead to a future with reduced energy footprints and enhanced performance, embodying the intersection of technology and sustainability.

Leave a Reply