As we navigate the 21st century, the urgency for sustainable energy sources has reached a critical level, primarily driven by the substantial rise in electric vehicle (EV) adoption. The challenge the automotive industry faces is no longer limited to merely converting traditional combustion engines to electric powertrains; it’s about ensuring that the very batteries that drive these vehicles are produced sustainably, without straining our planet’s resources. This shift toward sustainability is prompting researchers to explore innovative alternatives, particularly in the realm of lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries, which have long been the standard in energy storage technology.
Manganese: A Game Changer in Battery Technology
The increasing interest in manganese (Mn) as an electrode material for Li-ion batteries could signify a turning point in battery development. Unlike the conventional nickel (Ni) and cobalt (Co)-based batteries, manganese offers a more abundant and cost-effective option. Its integration into the battery composition brings a dual advantage of reducing costs while promoting environmental sustainability—a necessary consideration in a world grappling with resource depletion. By shifting focus to manganese, researchers are attempting not only to retain the high performances associated with nickel and cobalt but also to pioneer a more eco-friendly production technique that aligns with global sustainability goals.
New Insights into LiMnO2 Electrode Material
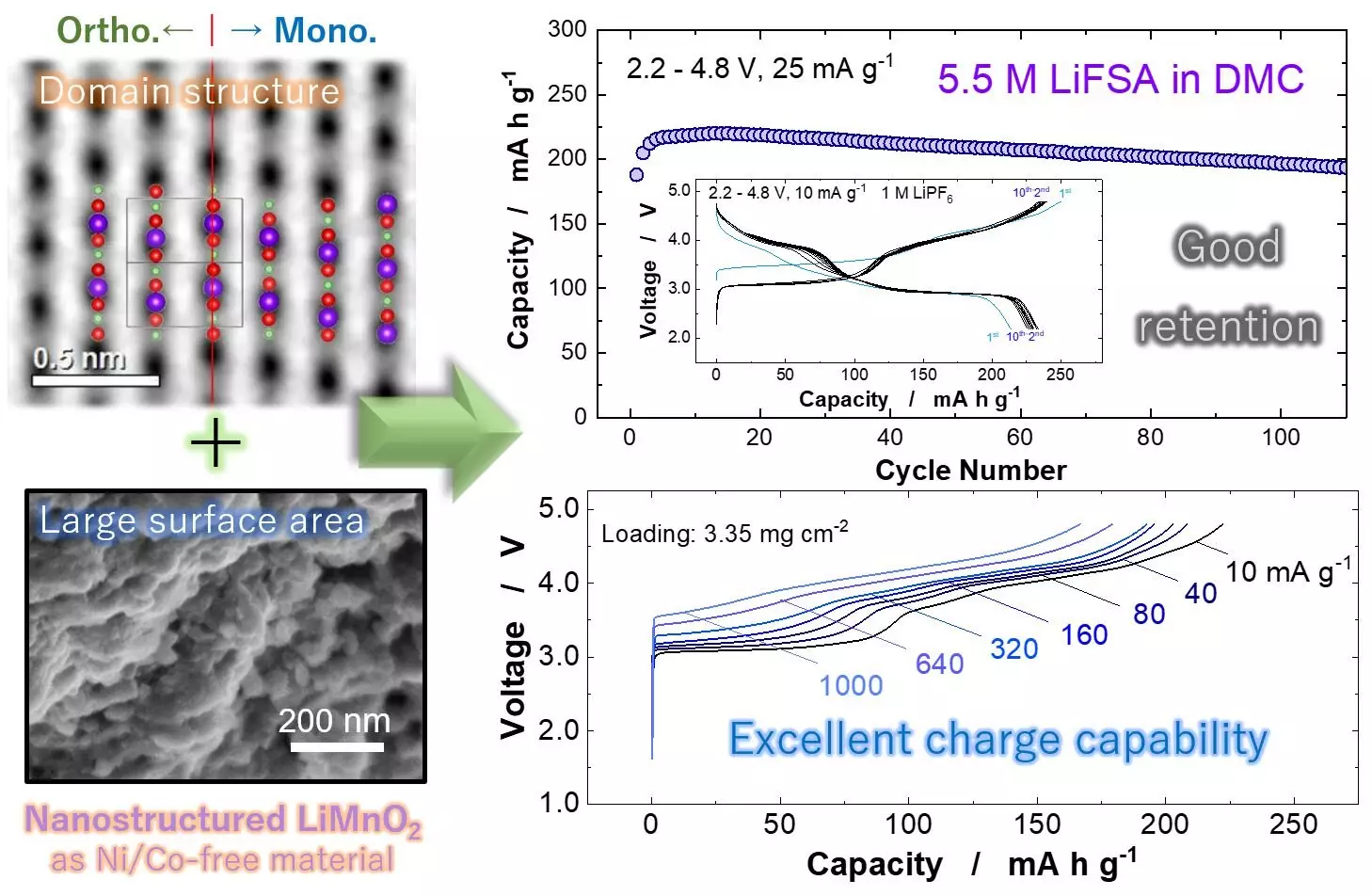
Recent research published in *ACS Central Science* on August 26, 2024, illuminates new avenues for enhancing the performance of LiMnO2, a polymorph of manganese oxide that has been subject to previous studies due to its potential as an electrode material. Traditionally, the application of LiMnO2 has been hindered by its limited performance, attributed primarily to restrictive crystalline structures. However, a detailed investigation into various LiMnO2 polymorphs has unveiled that a monoclinic layered domain can significantly uplift its structural and electrochemical performance.
This novel approach introduced by researchers, particularly Naoaki Yabuuchi, indicates that through systematic exploration and optimization of the LiMnO2 structure, it is possible to synthesize a nanostructured variant that efficiently undergoes desirable phase transitions. This capability not only enhances energy storage capacity but also establishes a direct synthesis method without intermediary steps—simplifying production processes and carving a path toward more economical manufacturing.
Impressive Performance Metrics
The implications of this research are striking. The newly devised nanostructured LiMnO2 achieves energy densities of up to 820 watt-hours per kilogram (Wh kg-1), outpacing its nickel-based counterparts, which typically hover around 750 Wh kg-1. This claim suggests that the potential for LiMnO2 to meet, and possibly exceed, the energy demands of future electric vehicles is within reach, while minimizing the reliance on more contentious materials like cobalt. These advantageously competitive energy densities make it a formidable contender in the rapidly evolving battery market.
Moreover, one of the persistent challenges faced by manganese-based batteries—voltage decay—seems to be absent in the case of the newly synthesized nanostructured LiMnO2. Voltage decay not only compromises battery efficiency but also undermines consumer confidence in battery longevity. The absence of such decay in this new material positions it as a promising option for various applications, especially in the demanding field of electric vehicles.
Addressing Potential Drawbacks
Despite the encouraging results, researchers must tackle the issue of manganese dissolution, a phenomenon that remains a concern in practical applications. The susceptibility of manganese to dissolve over time poses a risk to the battery’s longevity and overall effectiveness. Nevertheless, findings point towards feasible solutions, such as employing concentrated electrolyte solutions and applying lithium phosphate coatings to mitigate this problem. These strategies may help ensure a more reliable and durable battery product.
In light of these advancements, the potential for LiMnO2-based batteries to emerge as a sustainable alternative to traditional materials appears increasingly feasible. This could catalyze a shift in the EV industry, steering it toward greener solutions that not only provide energy efficiency but also lessen environmental impact, fulfilling the dual vision of sustainability and performance in modern transportation.
As researchers continue to refine and analyze these innovative materials, the future of electric vehicle batteries may center around the integration of manganese, shaping not only the landscape of electric mobility but also our approach to global sustainability in energy sources.

Leave a Reply