In recent years, researchers have tirelessly sought new avenues to enhance computing performance. With the rapid growth of data-driven industries, the need for speedier and more efficient computing systems has never been more critical. The pioneering research from a collaboration between Skoltech and Germany’s Bergische Universität Wuppertal unveils an innovative system utilizing a universal NOR logic gate powered by polariton condensates. This breakthrough holds the potential to reshape the fabric of computing, shift paradigms, and ultimately guide us toward a future dominated by optical technology.
The Mechanism Behind Polariton Condensates
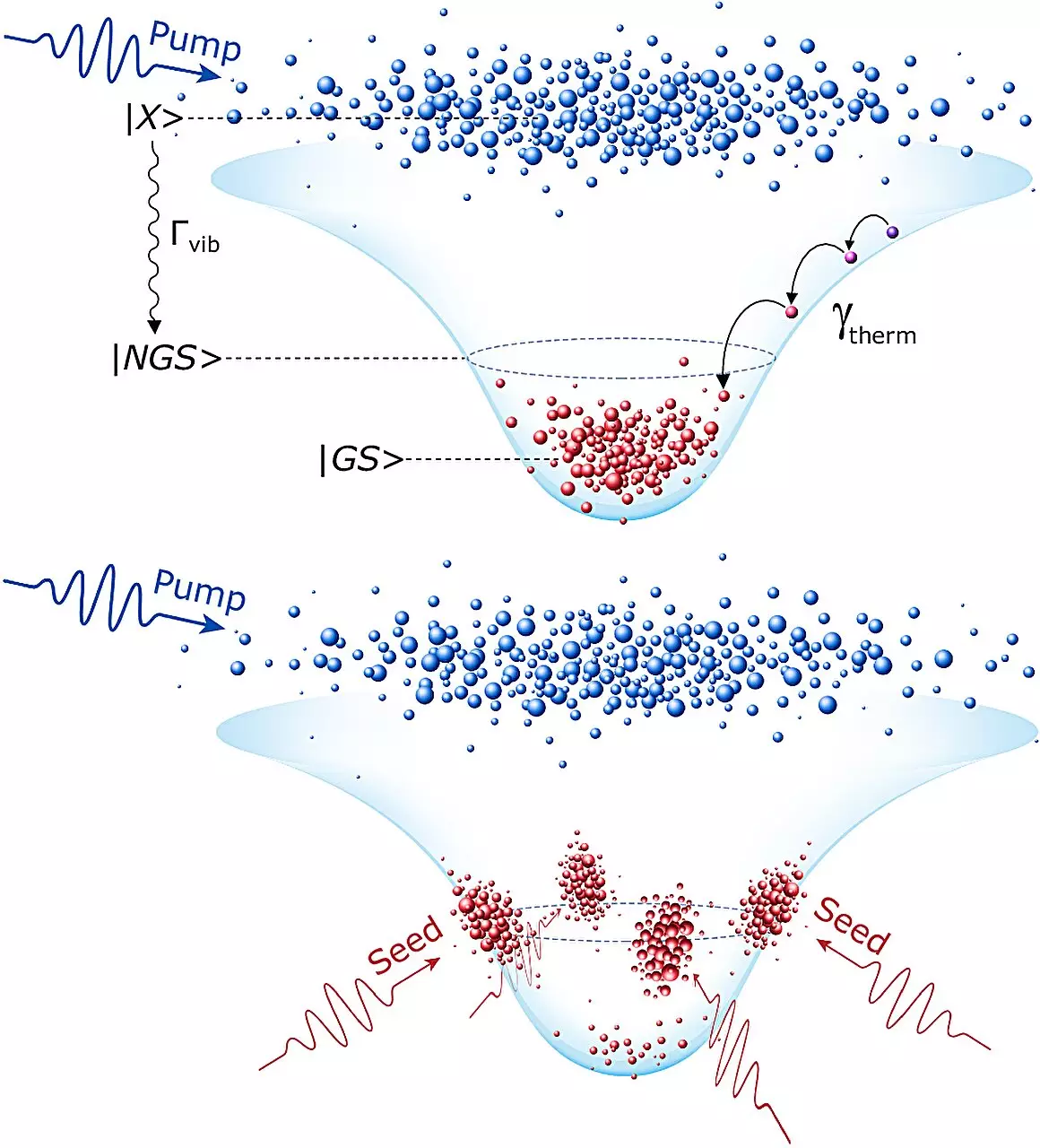
At the core of this innovative research lies polariton condensates—a hybrid state of matter created from excitons and photons that exhibits fluid-like qualities. Affectionately referred to as “liquid light,” these condensates allow for the manipulation of optical signals with remarkable efficiency. Unlike traditional electronic systems constrained by Ohm’s law, polariton condensates enable operations that transcend the limitations of mere electrons. While conventional electronic logic gates typically handle operations at frequencies capped around several gigahertz, the new optical gate operates at speeds reaching up to one terahertz—approximately 300 times faster.
The researchers’ ability to condense polaritons into both ground and excited states means they can accomplish tasks previously thought impossible in optical logic. This progress represents not merely an incremental improvement but a revolutionary transition toward an era where optical computing can be harnessed for complex, high-speed calculations.
NOR Logic Gates: The Powerhouse of Logic Operations
Logic gates serve as the cornerstone of digital circuits, facilitating various operations—conjunctions, disjunctions, and negations that are crucial for processor functionality. Traditional logic gates may have limited inputs, typically handling 2–8 at a time. However, the Skoltech team’s achievement in developing a universal optical NOR gate with adaptability for up to 12 inputs signals a significant advancement in the realm of computational efficiency. This multi-input capability could drastically enhance processing power, allowing for more complex operations without necessitating a larger physical circuit arrangement.
Moreover, the optical nature of this technology not only circumvents the burden of electric current but also suggests an eco-friendly approach to computing. By leveraging light, the impact of thermal dissipation is minimized, potentially leading to substantial energy savings—a critical factor in today’s environmentally-conscious technological development.
Challenges Overcome: The Physics of Light
The longstanding challenges in optical logic stem from the interactions (or lack thereof) among photons. Unlike electrons, which are subject to interactions that complicate their use in logical circuits, photons pass through each other without interference. This phenomenon has historically stymied the development of efficient optical logic converters, making breakthroughs like the one achieved by Skoltech’s team both impressive and significant.
Through innovative methodologies, the researchers have ingeniously fashioned a mechanism that can disable optical signals using light itself. This feat not only solves a critical problem in the development of optical logic but also exemplifies a broader trend in scientific inquiry: the ability to leverage fundamental principles of physics to devise innovative technological solutions.
Imagining the Future of Computing
The implications of these breakthroughs extend well beyond just faster processing speeds. An optical computing framework like the one being explored could revolutionize fields ranging from artificial intelligence to big data analysis. If successfully implemented in computing devices, this technology could enable real-time processing of vast amounts of information, fostering advancements in areas such as quantum computing, telecommunications, and machine learning.
As we stand on the brink of potentially transformative technology, the collaborative efforts of researchers underscore the importance of interdisciplinary approaches to innovation. Just as the digital revolution fundamentally changed how we interact with technology, optical computing offers a tantalizing glimpse into a future where speed and efficiency combine to yield unprecedented performance levels in computational tasks.
This exciting research published in the journal *Nature Communications* marks a significant step toward realizing the dream of optical computers capable of reshaping our digital landscape. The potential to craft machines that operate fundamentally differently, leveraging the unique properties of light, raises both questions and possibilities for how we approach computation in the decades to come. With every advance in this field, we inch closer to a new horizon in technological progress, illuminating paths previously shadowed by the constraints of conventional electronic systems.

Leave a Reply