In a significant advancement for environmental science, researchers at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science have unveiled an innovative microfluidic sensor array capable of detecting and visualizing multiple heavy metal ions in water with unprecedented efficiency. Led by Prof. Jiang Changlong, this groundbreaking study, detailed in the Chemical Engineering Journal, holds promising implications for water quality monitoring and public health.
The Heavy Metal Challenge
Heavy metals like mercury, lead, chromium, and copper pose formidable challenges to water systems around the world. These contaminants, often the byproducts of industrial processes, can infiltrate natural water bodies, threatening the ecosystem’s integrity and endangering human health. Their persistence in the environment is a cause for concern, as traditional detection techniques are not only time-consuming but also cumbersome, necessitating individual analysis for each metal—a method ripe for inefficiency.
Microfluidic Technology: A Game Changer
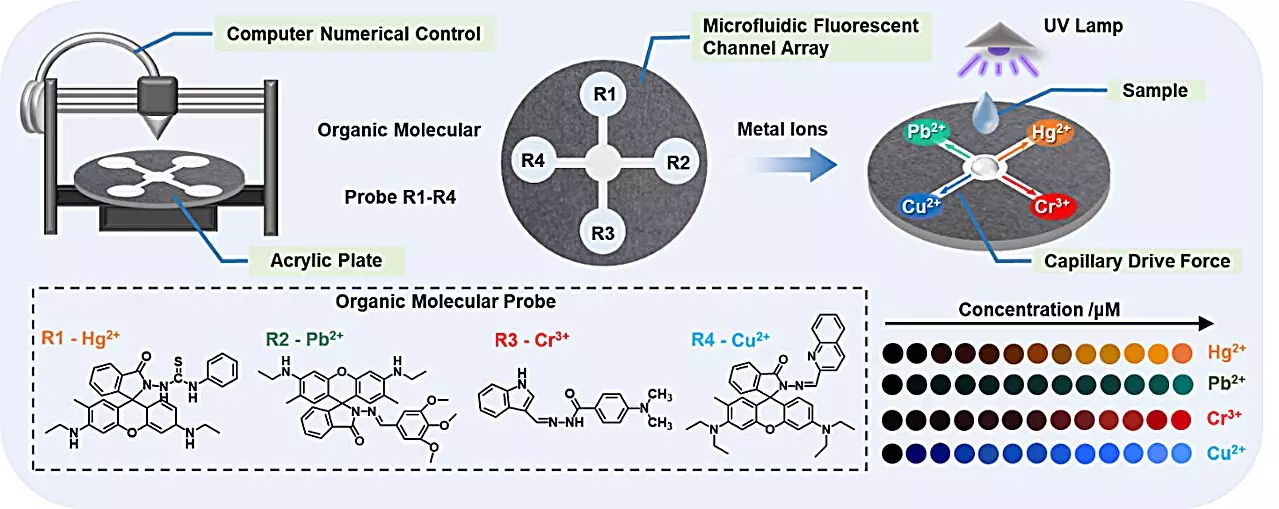
Addressing these challenges, the researchers have designed microfluidic sensors that utilize acrylic plates combined with capillary action and hydrophobic surfaces to create nuanced fluid channels. This novel configuration facilitates the simultaneous testing of multiple contaminants, streamlining what was once a labor-intensive process into something rapid and efficient. The synergy of microfluidics and fluorescent probes is the real triumph here, marking a pivotal shift in how we can approach water safety assessments.
The Power of Fluorescent Probes
At the heart of this innovative system are organic fluorescent probes that demonstrate remarkable sensitivity and specificity. By binding selectively to targeted heavy metal ions, these probes illuminate the contamination present in the water sample. With the ability to detect four distinct heavy metals at once, the sensor array not only broadens the scope of testing but promises real-time results that can be visualized instantaneously.
Integration with Everyday Technology
What sets this research apart is its compatibility with everyday technologies. With the use of a smartphone equipped with color recognition technology, the results of water testing become readily accessible. This integration brings scientific innovation into the hands of the general public, enabling individuals to monitor water quality in their own homes or communities. The paradigm shift from laboratory-based analysis to an accessible, user-friendly system could empower people to take control of their environmental health.
Implications for Environmental Safety
The implications of this research are twofold; not only does it enhance our ability to monitor water quality efficiently, but it also increases public awareness regarding the potential hazards of heavy metal contaminants. By simplifying the detection process, this technology paves the way for more comprehensive water safety initiatives, vital for communities that have previously lacked adequate monitoring tools. As we move forward, it is essential to embrace innovations like these, which promise to protect ecosystems while ensuring human health is prioritized in the face of industrialization.
In this new landscape of water quality management, the marriage of technology and environmental science stands as a beacon of hope, equipping society to tackle one of its most pressing challenges head-on.

Leave a Reply