In recent years, the world has witnessed an unprecedented rise in the adoption of renewable energy technologies, particularly solar photovoltaics (PV) and wind power. A report from the International Energy Agency (IEA) highlights a critical juncture in this renewable revolution, as government action is pivotal in ensuring that these growing energy sources are seamlessly integrated into existing power systems. Between 2018 and 2023, the global capacity for solar PV and wind energy has not only more than doubled but also significantly increased their contributions to overall electricity generation. This dramatic surge is largely driven by favorable government policies, technological advancements, and ongoing cost reductions, signaling a promising trajectory toward a greener future.
However, this rapid expansion presents a formidable challenge. As solar and wind energy sources are often variable—dependent on weather conditions and time of day—proper integration into power infrastructures is essential to fully harness their potential. Without a strategic approach, governments risk missing out on the substantial benefits these renewable sources can offer in combating climate change and realizing energy security goals.
Solar and wind energy stand at the forefront of efforts to reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the reductions necessary for achieving net-zero targets by the mid-century. Yet, the path toward maximizing these contributions is fraught with obstacles that policymakers must navigate. A crucial finding of the IEA report is that a failure to implement essential support measures for the integration of solar and wind energy could lead to a 15% reduction in projected generation by 2030, allotting a significant drawback to global electric grid efficiency.
Keisuke Sadamori, the IEA’s Director of Energy Markets and Security, emphasizes that a continued increase in renewable energy capacity requires robust integration efforts. While the pace of growth is encouraging, realizing the full benefits of these technologies hinges on government and institutional commitment to establishing strong integration frameworks.
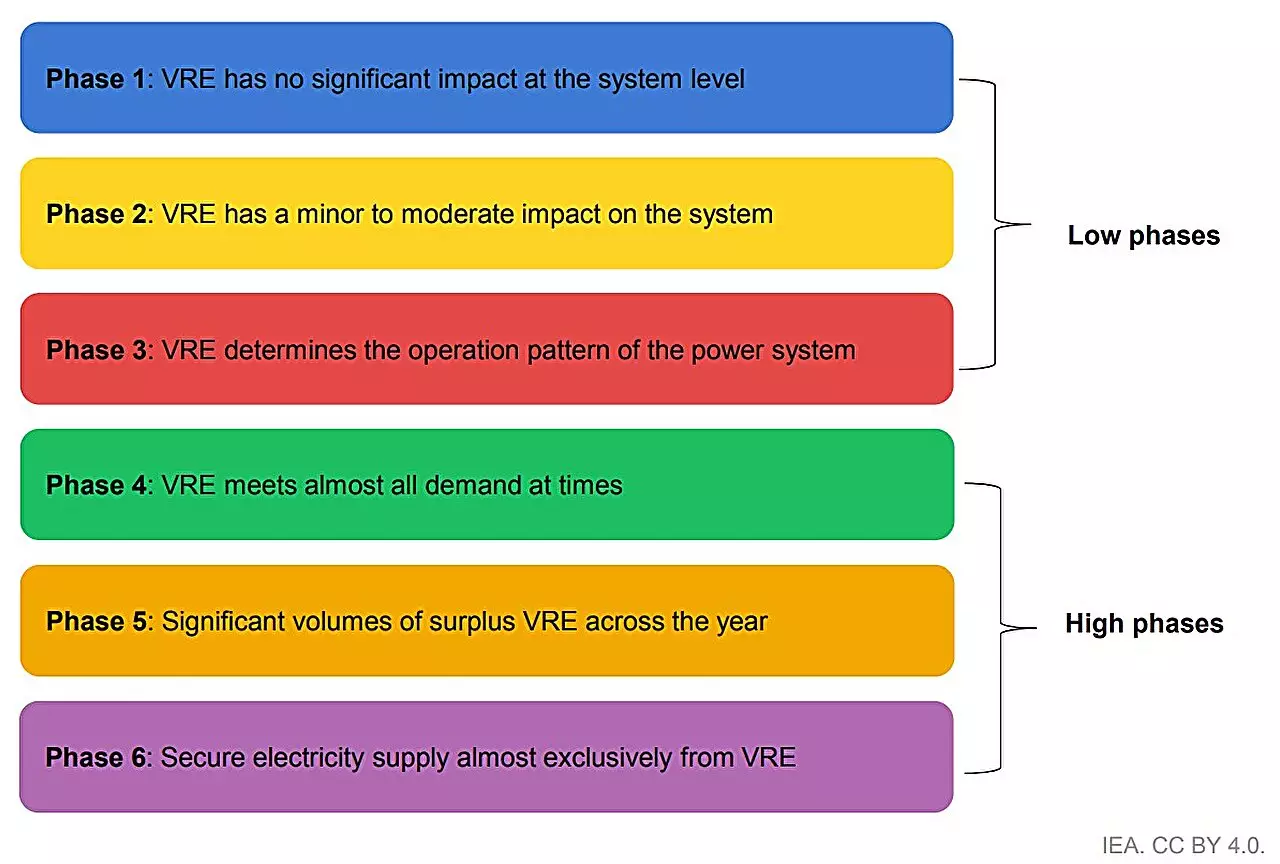
A noteworthy aspect of the IEA report is its comprehensive assessment of integration measures across 50 diverse power systems, collectively responsible for roughly 90% of worldwide solar PV and wind generation. This landmark analysis illustrates a broad spectrum of approaches being taken to facilitate greater incorporation of variable renewable energy into national grids. Countries that currently utilize a minimal share of renewables still have the potential to drive considerable generation growth through manageable enhancements rather than overwhelming overhauls of their energy systems.
Proven strategies, such as improving the flexibility of existing energy assets and enhancing forecasting capabilities, appear to yield effective results when applied gradually in response to evolving demands. Yet, as renewable penetration reaches increased levels, these systems often face heightened challenges.
Pioneering energy systems like Denmark, Ireland, and Spain have paved the way by experimenting with innovative solutions to overcome the integration barriers associated with high levels of solar and wind power. The development of energy storage technologies and advanced grid solutions forms a critical part of the toolkit for managing the inherent fluctuations in output from renewable sources. As the IEA report notes, most technological responses to these integration difficulties are either already established or approaching maturation. The shift toward effective integration is less about groundbreaking innovations and more about aligning existing technologies with appropriate policy frameworks.
Yet, a fundamental rethink of traditional planning and operational methodologies is essential to accommodate increasing reliance on variable renewables. Policymakers must prioritize not only technological deployment but also the regulatory changes necessary to support a more integrated energy future.
As the world continues to witness an exponential rise in renewable energy capacity, the onus lies upon policymakers, regulators, and stakeholders to develop viable integration strategies. Fostering an adaptive regulatory environment, investing in grid enhancements, and embracing innovative technology will be critical in ensuring that solar and wind can play a transformative role in the energy landscape. The time to act is now, as the momentum toward renewable energy deployment offers a unique opportunity to reshape energy systems globally, targeting substantial economic and environmental benefits along the way.

Leave a Reply