The emergence of hybrid perovskites marks a significant milestone in the development of high-efficiency electronic devices, particularly in the fields of photovoltaics and light-emitting diodes (LEDs). However, a critical challenge that persists is the longevity of these materials under operational conditions. As they undergo aging, their efficiency diminishes, thus impeding their viability for extensive commercial applications. Understanding the aging process and identifying effective stabilization techniques are essential for bridging the gap between laboratory developments and successful market integration.
Hybrid perovskites, known for their remarkable optoelectronic properties, face a paradox: despite their impressive performance metrics, their practical use is curtailed by substantial instability. Factors such as environmental moisture and temperature fluctuations accelerate the degradation of these materials, resulting in decreased performance over time. For researchers and companies alike, the pressing issue is not merely to enhance the stability of perovskites, but also to devise reliable methodologies for real-time aging assessment. Gaining insights into the degradation mechanisms is pivotal for creating more robust and efficient devices that can endure the rigors of daily use.
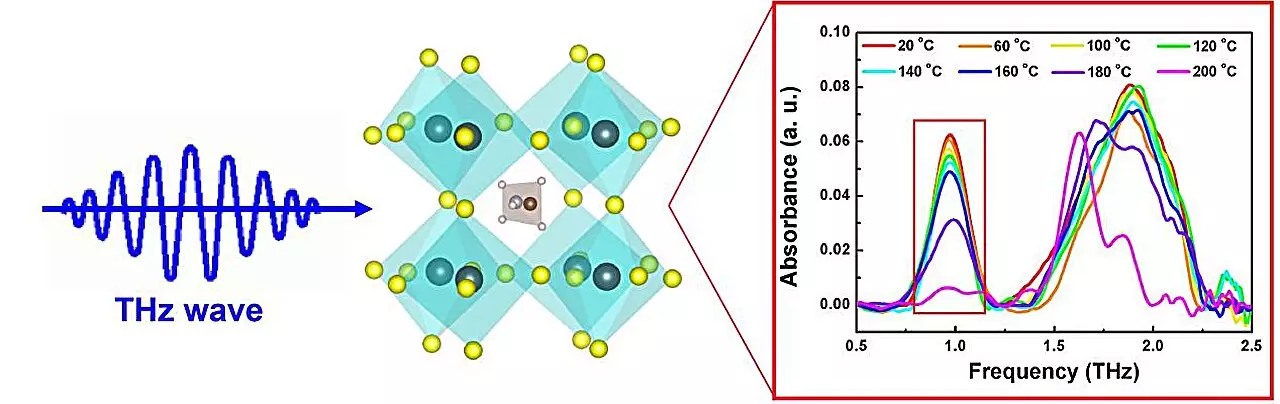
In a groundbreaking study conducted by a research team led by Prof. Yiwen Sun at Shenzhen University, the use of terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS) is highlighted as an innovative approach to monitor the aging of perovskites in real-time. Terahertz waves can interact with the phonon vibrations within the perovskite structure, providing intricate details about the material’s physical state. The research, published in *Frontiers of Optoelectronics* on July 29, 2024, emphasizes the correlation between the phonon vibration modes and the Pb-I bonds within the perovskite. As these bonds weaken with aging, the intensity of the corresponding terahertz absorption peaks alters, presenting an opportunity to quantify the aging process.
Implications for Future Developments
The proposed strategy of leveraging terahertz absorption peaks as indicators of perovskite aging is not just a theoretical framework—it offers practical applications that could revolutionize product development. By establishing a real-time feedback loop regarding material integrity, manufacturers can optimize the formulation of perovskite materials for enhanced longevity. Consequently, this could expedite the commercialization process of perovskite-based devices, fostering their transition from experimental systems to everyday technologies.
Furthermore, the ability to monitor aging could simplify quality control processes and enhance consumer confidence in new perovskite applications. As the sector moves towards larger-scale production, understanding the degradation mechanisms will empower researchers to innovate further, potentially leading to next-generation perovskite materials that outperform existing alternatives.
Addressing the challenges of hybrid perovskite longevity through real-time aging detection represents a pivotal advancement in the field of electronic devices. The innovative approach demonstrated by Prof. Sun and his team illustrates a critical step towards making perovskites more reliable and commercially viable. As the technology matures, its potential to transform renewable energy solutions and lighting efficiency remains profoundly promising. By focusing on improving both stability and real-time monitoring, the industry can unlock the full capabilities of hybrid perovskites, paving the way for a sustainable electronic future.

Leave a Reply