For years, researchers have grappled with the enigmatic relationship between mitochondrial dysfunction and Parkinson’s disease, a condition that affects millions worldwide. In a groundbreaking study, scientists at the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research (WEHI) in Australia have shed light on the elusive PINK1 protein, critical to cellular energy efficiency and implicated in early-onset Parkinson’s disease. Their work utilizes cutting-edge imaging techniques, illuminating the structural nuances of PINK1 and how it interacts with mitochondria—the cellular powerhouses that are essential for brain function. This revelation isn’t just a minor advancement; it’s a pivotal moment in Parkinson’s research that could alter the future of therapeutic strategies.
The Mysteries of PINK1 Unraveled
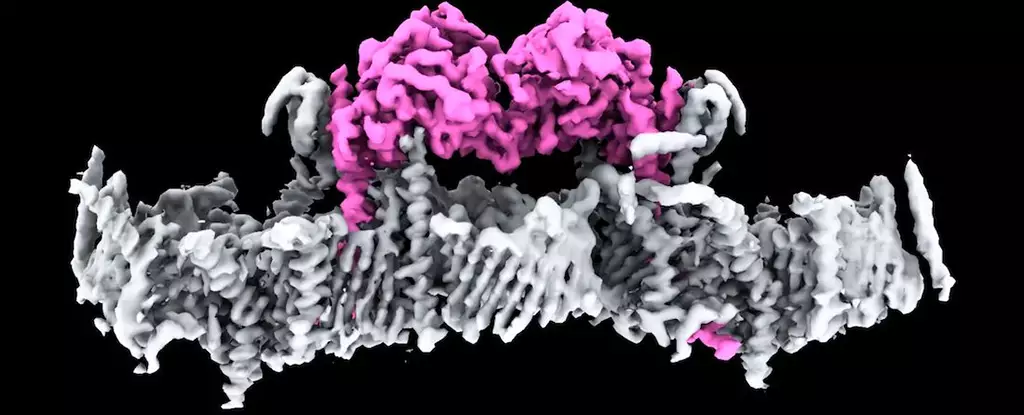
For over two decades, the PINK1 protein has been a focal point of Parkinson’s disease research, primarily because mutations in its gene are known to cause early-onset forms of the disease. However, the molecular processes behind these mutations have remained largely mysterious. The recent findings from WEHI have systematically unraveled these processes, demonstrating how PINK1 forms partnerships with cellular components to fulfill its essential functions. Specifically, the team employed cryo-electron microscopy to visualize the structure of PINK1 when it binds to damaged mitochondria, showcasing a previously unseen docking mechanism that is foundational to its role as a protector of cellular health.
As PINK1 navigates through the mitochondrial membranes, its normal operations involve working seamlessly to identify and eliminate dysfunctional mitochondria. This function is crucial, especially in the brain, which demands constant energy replenishment to maintain cognitive functions. The research shows that when PINK1 malfunctions due to genetic mutations, this critical disposal mechanism falters, leading to the accumulation of defective mitochondria. This accumulation is particularly detrimental to neurons, contributing to neurodegeneration characterized by Parkinson’s disease.
Significance of Advanced Imaging Techniques
The significance of advanced imaging techniques in this research cannot be overstated. By employing methods such as mass spectrometry alongside cryo-electron microscopy, researchers achieved a high-resolution view of protein interactions at the mitochondrial surface. They discovered the importance of a specific protein complex known as TOM-VDAC as the docking site for PINK1. This intricate mechanism of binding highlights the sophisticated nature of cellular processes that underpin energy regulation in neurons. It exemplifies how scientific inquiry can lead to essential discoveries that potentially pave the way for new therapeutic approaches.
This research also lays the groundwork for future studies aimed at developing treatments that focus on repairing or enhancing PINK1 function. If successful, such treatments could significantly alter the progression of Parkinson’s disease, improving the quality of life for those afflicted. The knock-on effects of these advancements could extend beyond Parkinson’s; therapies that target mitochondrial dysfunction may offer solutions for other neurodegenerative diseases linked to similar mechanisms.
A Community of Molecules: Connecting the Dots
Understanding PINK1’s interactions opens a broader conversation about the collective role of mitochondrial proteins and cellular signaling in disease. Parkinson’s disease is notoriously complex, and while PINK1 is a critical player, it is only one piece of a larger puzzle involving numerous contributing factors. By elucidating the mechanisms of proteins like PINK1, researchers are more likely to discover common pathways that unify the various causes of Parkinson’s and potentially lead to more holistic treatment options.
The early-stage discoveries announced by the WEHI team have ignited excitement amongst the scientific community, as they emphasize the interconnectedness of cellular health and neurodegenerative diseases. By connecting these molecular dots, researchers can explore therapeutic avenues that were previously unfathomable, lighting a path forward in the fight against diseases that not only affect individuals but also families and communities at large.
The implications of this research stretch far beyond academic interest; they represent a beacon of hope for millions of individuals battling Parkinson’s disease as well as their families. The potential to alter the course of this debilitating condition through innovative science underscores the importance of continued investment in basic research. The data emerging from this study encircle the promise of improving lives, a pursuit that scientists and society must rally around with urgency and enthusiasm.

Leave a Reply