At the heart of chemistry lies a complicated dance of atoms and molecules, the fundamental building blocks of our universe. These entities are not just simple spheres or particles; they are intricate quantum systems that require a profound understanding of the behavior of electrons. This highly complex structure poses challenges that have long confounded scientists. Recent advancements in machine learning have opened new avenues for tackling these challenges, enabling researchers to simulate molecular dynamics with unprecedented accuracy and efficiency. The implications of such breakthroughs could revolutionize fields ranging from pharmaceuticals to advanced materials, yet the complexity of quantum interactions still presents a formidable barrier.
The Power of Machine Learning in Chemistry
A collaborative effort between researchers at the Berlin Institute for the Foundations of Learning and Data (BIFOLD) and Google DeepMind has led to the creation of a novel machine learning algorithm that simplifies the daunting task of simulating molecular interactions. Traditional methods necessitate meticulous solutions to the Schrödinger equation, a mathematical framework that governs quantum behavior. However, the demands of solving these equations scale dramatically with the number of atoms involved—a challenge that even supercomputers struggle to overcome. This is where machine learning steps in, shifting the paradigm from explicit modeling of electron interactions to predictive learning that requires significantly fewer computational resources.
By leveraging data-driven methods, the new algorithm not only accelerates the simulation process but also enhances its accuracy. Researchers can now predict molecular behaviors over extended time scales, a feat that was previously considered nearly impossible due to the extensive computational requirements. As highlighted by BIFOLD researcher Thorben Frank, achieving this level of simulation would eliminate costly and laborious experimental procedures, thereby transforming how we approach chemical research.
Decoupling Complexity: A Novel Approach
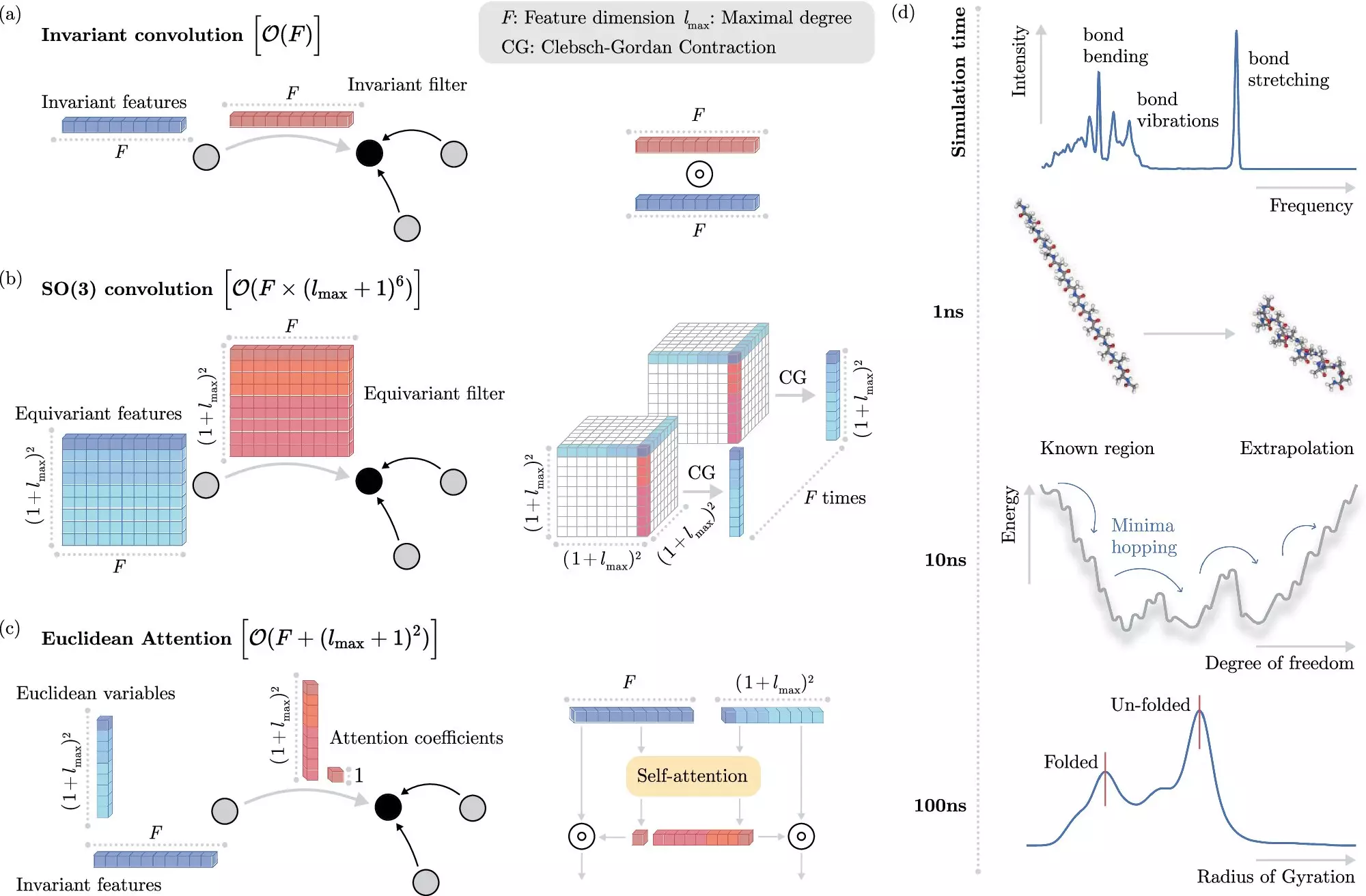
Traditional molecular simulations are often bogged down by the computational overhead of extracting invariant properties that might not directly contribute to the essential physics of the system under study. The newly developed machine learning approach from BIFOLD pioneers a different methodology by decoupling these invariances at the outset. This innovative tactic allows the algorithm to focus on core interactions that are critical while streamlining the process of simulating molecular dynamics.
Dr. Stefan Chmiela, a leading figure in this research, points out the dramatic improvements in efficiency. With the advancement of this machine learning algorithm, simulations that once required extensive processing time on high-performance computers can now be completed in mere days on a single node. Such efficiency is groundbreaking, allowing scientists to probe complex atomistic systems in ways that were previously untenable.
From Theory to Application: Drug Development and Beyond
One of the most promising applications of these enhanced molecular dynamics simulations lies in drug development. The ability to accurately simulate molecular interactions with proteins in the human body could significantly streamline the process of discovering new medications. The traditional route of empirical experiments is not only time-consuming but also costly and often laden with environmental concerns. By utilizing machine learning algorithms to predict interactions, researchers could potentially reveal new drug candidates more swiftly and sustainably.
The practical capabilities of this algorithm were vividly illustrated when researchers identified the most stable form of docosahexaenoic acid, an essential fatty acid critical for brain health. This task, requiring the examination of thousands of molecular candidates, would have been exceedingly arduous with conventional quantum mechanical methods. The advancement highlights how cutting-edge machine learning can turn theoretical possibilities into tangible reality.
Charting the Future of Computational Chemistry
As we move forward, the quest for more precise simulations will necessitate further evolution of these machine learning algorithms. Future iterations will be expected to accurately mirror complex, long-range interactions that define chemical systems at scale. These advancements hark back to a broader question: how can we harness the power of artificial intelligence to unravel the complexities of the physical world?
This research not only emphasizes the confluence of cutting-edge technology and foundational chemical principles but also underscores a vital shift towards realizing practical applications that can influence a multitude of sectors. As articulated by BIFOLD co-director Prof. Dr. Klaus-Robert Müller, this research embodies a crucial direction for scaling machine learning approaches that adequately meet the needs of complex chemical systems. With continued innovation, the horizon of computational chemistry promises to grow ever more inviting and fruitful—a testament to the extraordinary potential that lies at the intersection of artificial intelligence and scientific exploration.

Leave a Reply