Access to clean and safe drinking water has become an urgent global challenge as populations escalate and industrial activities pollute water sources. Each year, millions suffer from waterborne diseases, a dire consequence of insufficient purification technologies. Traditional methods are often generalist, treating large volumes of water but failing to distinguish between harmful and harmless substances. As a result, the ongoing water crisis calls for innovative solutions that prioritize both efficacy and specificity in water treatment.
Phytochelatin: Nature’s Genius at Work
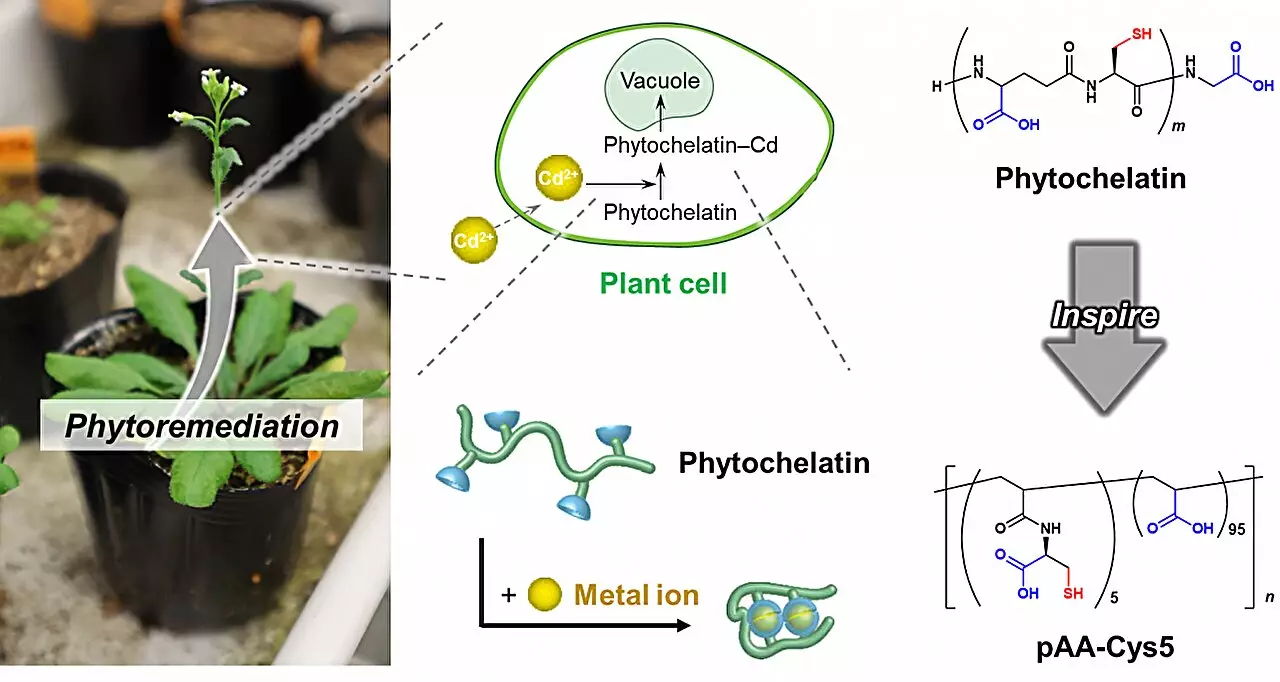
The innovative research from the HeKKSaGOn Alliance shines a light on a remarkable protein from the plant kingdom: phytochelatin. A natural protector, this protein adeptly binds to heavy metal ions, neutralizing their toxic impact on plant cells. This study prompts us to rethink our approach to water purification and harness the inherent wisdom that evolution has imbued in living organisms. By delving into phytochelatin’s molecular structure, particularly its unique ability to selectively bind cadmium ions—one of the most hazardous contaminants—the researchers have opened a door to a new era in water purification technology.
The Breakthrough: Polymer Synthesis Through Plant Inspiration
Leading the charge in this research is Dale Nakahata and his team, who have ingeniously synthesized a polymer inspired by the intrinsic qualities of phytochelatin. By analyzing its building blocks, the researchers pinpointed critical groups that contribute to its functionality—namely, carboxylate and thiolate groups. The brilliance of this study lies not just in mimicking nature but enhancing it. The team attached the polymer to silica beads and cellulose membranes, creating a highly concentrated solution capable of targeted ion removal. The implications of this breakthrough are monumental, promising a significant leap in the capabilities of existing water treatment technologies.
Efficiency in Action: A Game-Changer for Water Safety
When tested, the polymer exhibited an astounding ability to reduce cadmium levels in contaminated water. Within just one hour, the system successfully achieved drinking-water standards, even as it preserved essential minerals like magnesium and calcium. This specificity is a game-changer in an industry where overzealous purification can strip water of its necessary components. The study underscores the advantages of leveraging a flow-through approach, significantly increasing loading capacity and rate of purification, while minimizing the unwanted removal of beneficial ions. This innovation embodies a thoughtful balance between achieving safety and maintaining water quality.
Beyond Cadmium: Expanding the Horizons of Heavy Metal Removal
What makes this polymer particularly compelling is its potential applicability to other toxic heavy metals as well, especially mercury. With increased industrial discharge worldwide contributing to the contamination of water systems, developing a versatile solution that tackles multiple heavy metals could be transformative. The research team’s findings not only pave the way for addressing current contaminants but also allow for proactive measures against future pollutants, reflecting a deep understanding of the challenges faced in environmental health.
Lessons from Nature: A New Paradigm for Environmental Solutions
The research emphasizes a pivotal lesson in sustainability: solutions to significant problems often lie within nature itself. This study exemplifies how, by examining and mimicking biological systems, scientists can engineer improved technologies that don’t merely replicate existing methods but outshine them. As Tanaka aptly notes, the clever and sophisticated machinery developed by evolution often holds keys to current technological barriers. This inspires a horizon where further exploration into natural systems for environmental solutions could yield significant advancements.
Looking to the Future: A Watershed Moment for Clean Water
With the demand for clean water rapidly increasing, the implications of this polymer technology are profound. It signifies a turning point in water treatment methodologies, suggesting that a renewed focus on biomimicry could lead to novel solutions that are not only efficient but also environmentally sustainable. The marriage of science and nature could transform our approach to one of humanity’s most pressing dilemmas, ensuring that clean drinking water remains accessible for present and future generations. The future of water purification looks bright, fueled by innovation inspired by nature itself.

Leave a Reply