Recent advancements in the field of digital data encoding and storage have led to the creation of a groundbreaking system that combines microcapsules filled with luminescent dyes and phase change materials. This cutting-edge technology, spearheaded by a collaborative team of scientists, promises to enhance various applications, particularly in cybersecurity and anti-counterfeiting measures. By revolutionizing traditional data storage methods, this new system stands to offer solutions that are not only efficient but also cost-effective.
The pioneering research was conducted by a distinguished team including Dr. Claudio Roscini, a senior researcher, and Prof. Daniel Ruiz-Molina, the group leader at the ICN2 Nanostructured Functional Materials Group. Joined by experts from the Chemistry Department at the Autonomous University of Barcelona, such as Prof. Jordi Hernando and Dr. Jaume Ramón Otaegui, their collective expertise has led to the publication of their findings in the prestigious journal, *Advanced Functional Materials*. The collaboration underscores the interdisciplinary nature of scientific breakthroughs in the modern era.
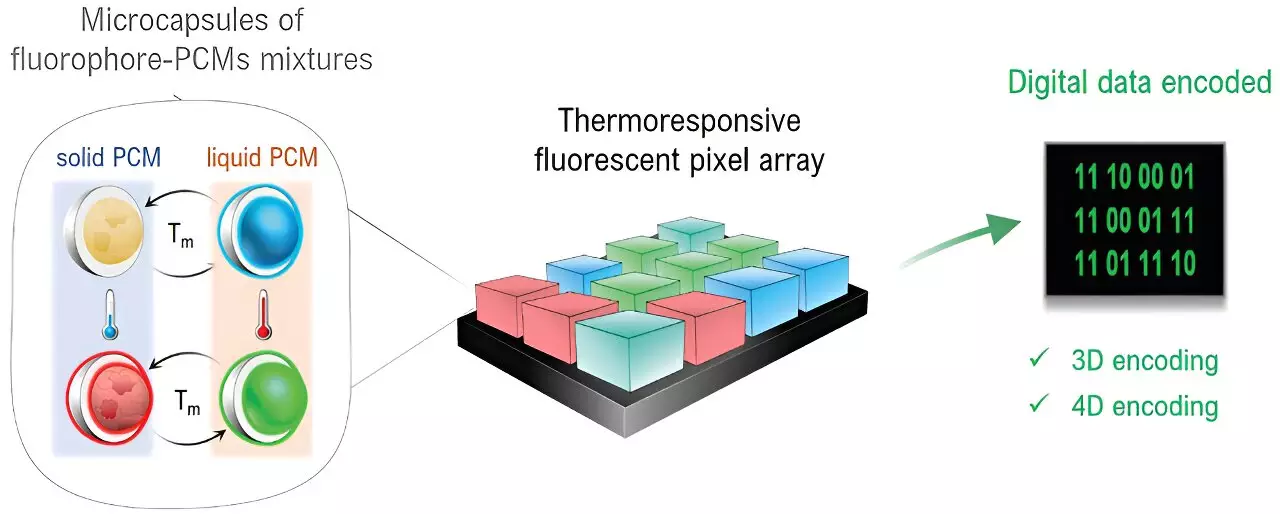
At the heart of this novel encoding system lies an innovative pixel technology leveraging microcapsules that contain a blend of fluorescent dyes along with phase change materials, such as paraffins. These phase change materials are well-known for their unique ability to absorb and emit thermal energy, providing a dynamic component to the encoding process. By manipulating the transition phases of these materials, researchers developed a method to encode data through variations in color emitted, directly tied to changes in temperature.
One of the most intriguing aspects of this new technology is its capability to execute advanced data encoding operations simultaneously across multiple dimensions. The encoding system operates in a three-dimensional space, using the two-dimensional positioning of pixels—similar to QR codes—enhanced by the three-dimensional color variations that arise from different dyes. Uniquely, an additional fourth dimension is introduced through temperature response, allowing for a more sophisticated encoding method. This four-dimensional approach to data storage could revolutionize how information is managed and retrieved.
The potential applications of this breakthrough extend well beyond conventional data storage methods. Industries reliant on anti-counterfeiting measures could greatly benefit from the complexity and efficiency of this technology. Similarly, high-density data storage solutions will become increasingly viable due to the novel encoding system’s low-cost yet high-efficiency approach. As global data needs expand, innovative systems such as these may provide the necessary infrastructure to safeguard and manage information securely.
The development of this advanced digital encoding and data storage system marks a significant leap forward in both technological innovation and practical application. With the capability to encrypt and store data through a unique combination of physical properties and dimensions, the contribution of this research team might very well lead to a new era in data management. As researchers continue to explore further possibilities, we may find ourselves on the brink of a revolution in how digital information is crafted, secured, and utilized across various industries.

Leave a Reply