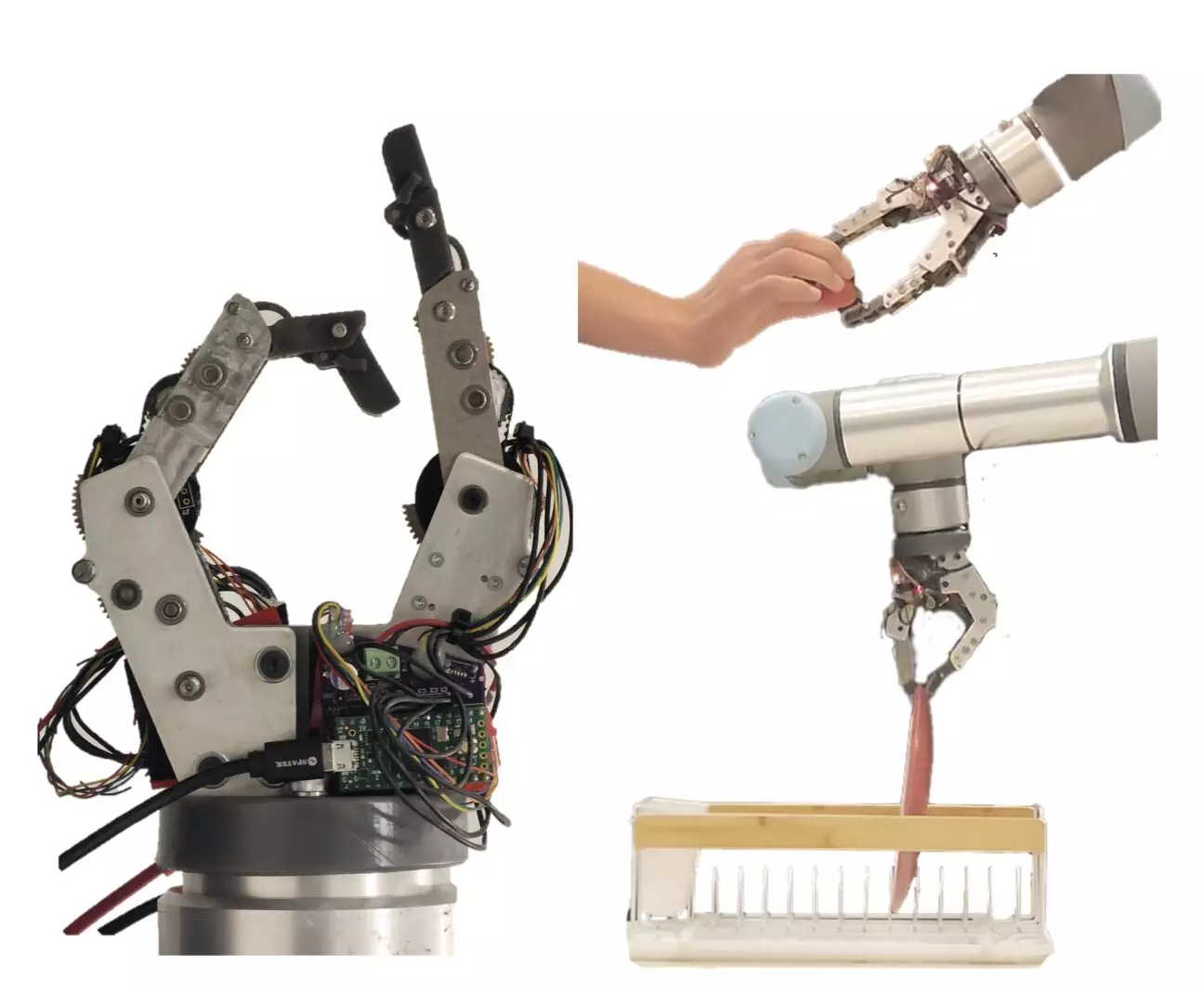
The creation of effective robotic systems that can manipulate objects in real-world settings is crucial for assisting humans in daily tasks. A recent project by researchers at Improbable AI Lab and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) focused on designing a new two-finger robotic gripper to enhance the dexterity of robots in handling everyday manipulation tasks.
The researchers aimed to meet the mechanical and dynamical requirements for a robotic finger capable of performing various everyday tasks. They introduced a finger design based on series-elastic actuation, known as the everyday finger, to attain the desired performance while keeping the fingers compact. The structure of the robotic gripper consisted of two human-like fingers that could bend and grasp objects effectively, mimicking the capabilities of human hands.
Initially, the gripper only had 2 degrees of freedom (DoF) due to the constraints of fitting multiple fingers onto a robotic hand. The researchers acknowledged the potential for future iterations to include additional fingers with more DoF, but highlighted the challenges in accommodating the size of the palm and the need for torque-dense actuators to support a full five-finger hand design.
To evaluate the performance of their two-finger gripper, the researchers conducted real-world experiments that assessed its speed, compliance, and force exertion during basic “pick-and-place” tasks. These tasks included picking up dishes, thin objects like paper, and delicate items such as strawberries. The results of the experiments demonstrated the gripper’s successful performance in completing the assigned tasks, indicating its potential for use in basic household robots.
While the initial tests showcased the capabilities of the two-finger robotic gripper in handling simple tasks, the researchers acknowledged the need for further design improvements and extended evaluations to broaden the range of daily tasks the gripper can effectively manage. By enhancing the gripper’s design and testing it on more complex scenarios, the researchers can refine its functionality for broader practical applications.
The development of a two-finger robotic gripper by researchers at Improbable AI Lab and MIT presents a promising advancement in enhancing robotic manipulation capabilities for everyday tasks. Despite the limitations in degrees of freedom and the simplicity of the tasks evaluated in the initial experiments, the results indicate a potential pathway towards developing more sophisticated robotic systems for assisting humans in various practical settings. By continuing to innovate and refine the gripper design, researchers can contribute to the evolution of robotic technology for improved human-robot interactions.

Leave a Reply